LED lighting is a beacon of innovation, casting a new light on how we illuminate our surroundings. This transformative technology has reshaped the lighting landscape with its unparalleled energy efficiency and longevity.
Historical Evolution and Modern Advances of LED Lighting
LED lighting, standing for Light Emitting Diode, has revolutionized the way we think about lighting solutions.
Tracing the lineage of LED technology reveals a story of relentless innovation and progress. The inception of LED technology can be traced back to the early 1960s, with the development of the first visible-spectrum LED in a vivid red hue. This initial breakthrough laid the groundwork for future advancements, culminating in the seminal invention of the blue LED in the early 1990s. This pivotal discovery unlocked the potential for white LEDs, catalyzing a paradigm shift in the lighting industry.
At its core, LED technology harnesses the power of semiconductors to convert electricity directly into light, bypassing traditional methods that rely on heating filaments or exciting gases. This technological leap translates into a highly efficient, low-heat lighting solution that outperforms traditional incandescent and halogen bulbs. The direct conversion process intrinsic to LEDs not only maximizes energy efficiency but also aligns with a growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly lighting options. From illuminating cozy living spaces to brightening expansive commercial areas, LED lighting offers a versatile and greener alternative for a myriad of lighting needs.
Today, the trajectory of LED technology continues to ascend, driven by ongoing research and innovations that enhance its efficiency, color spectrum, and adaptability. LEDs now play a pivotal role in smart lighting systems, urban infrastructure, and even artistic lighting projects, underscoring their integral position in the future of lighting.
How Do LEDs Work?
Delving into the workings of LED technology uncovers the fundamental principles that set it apart from conventional lighting methods.
Basic Principles of LED Technology
The essence of LED technology is encapsulated in the phenomenon of electroluminescence, where specific materials emit light when an electric current passes through them or when they are subjected to an electric field. This principle of generating light through electron movement across semiconductor materials is what fundamentally differentiates LEDs from traditional lighting solutions. The electroluminescence process in LEDs is marked by efficiency and minimal heat production, contributing to their extended lifespan and enhancing their safety profile. By leveraging this advanced technology, LEDs offer a significant leap forward in lighting, combining energy conservation with superior performance.
Comparison with Traditional Lighting Methods
When contrasted with conventional lighting technologies, LEDs present a stark divergence in terms of operation and efficiency. Traditional incandescent bulbs rely on the principle of heating a filament to emit light, a process inherently fraught with inefficiency due to the substantial loss of energy as heat. Fluorescent lighting, while an improvement over incandescent bulbs, still entails the excitation of gases and the conversion of UV light to visible light through a phosphor coating, a process that is not without its own set of inefficiencies and environmental concerns. LEDs transcend these limitations by offering a method of light production that is not only more energy-efficient but also environmentally friendly, marking them as the preferred choice for sustainable and effective lighting solutions in a variety of applications.
Advantages of LED Lighting
The shift towards LED lighting is driven by a constellation of benefits that extend far beyond mere illumination. These advantages position LEDs not just as a technological advancement but as a pivotal movement toward more sustainable, efficient, and adaptable lighting solutions.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
At the forefront of LED innovation is the unparalleled energy efficiency that these light sources offer. LEDs have redefined the benchmarks for power consumption in lighting, requiring significantly less energy to emit the same, if not greater, levels of brightness as their incandescent and fluorescent counterparts. This leap in efficiency not only aligns with global efforts to reduce energy consumption and mitigate environmental impact but also translates into tangible economic benefits for both individual consumers and businesses. The lower energy requirements of LEDs mean that lighting, one of the most widespread energy demands in both residential and commercial settings, becomes markedly less costly, contributing to broader energy conservation goals and financial savings.
The economic case for LEDs is compelling, particularly when considering the total cost of ownership over the lifespan of the lighting solution. While the upfront cost of LED fixtures and bulbs may be higher than traditional lighting options, the long-term savings realized through reduced energy consumption and the infrequency of replacements make LEDs an undeniably cost-effective choice. The longevity of LED bulbs, often rated for tens of thousands of hours of use, means that the initial investment pays dividends in the form of lower utility bills and decreased maintenance and replacement costs, offering a substantial return on investment that justifies the initial expenditure.
Durability and Minimal Environmental Footprint
The robustness of LED technology is a key factor in its appeal. LEDs are designed to withstand a wide range of conditions, contributing to their extended lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacements. This durability translates into less maintenance, particularly in commercial or industrial settings where lighting fixtures may be inaccessible or difficult to service. The long service life of LEDs, coupled with their reliability, ensures consistent lighting performance over time, making them a preferred choice for a wide array of applications.
The environmental advantages of LEDs cannot be overstated. By consuming less energy, LEDs play a direct role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity production. Furthermore, the absence of toxic materials like mercury in LEDs alleviates concerns related to disposal and environmental contamination. The extended lifespan of LED bulbs also means less waste, contributing to a reduction in the environmental footprint of lighting solutions. Collectively, these attributes underscore the role of LED lighting in fostering a more sustainable and responsible approach to illumination, aligning with broader environmental conservation goals.
Optical Delivery Efficiency
Beyond their economic and environmental benefits, LEDs stand out for their optical delivery efficiency. The inherent design of LEDs allows for precise control over light direction, minimizing light spill and focusing illumination exactly where it is needed. This precision is invaluable in both architectural and functional lighting design, enabling the creation of atmospheres and environments that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally optimal. The ability of LEDs to direct light efficiently enhances the effectiveness of lighting designs, reducing waste and ensuring that light serves its intended purpose with maximum impact.
Spectral Engineering and Color Rendering
The versatility of LEDs extends into the realm of spectral engineering and color rendering, where they truly shine. LEDs offer an unparalleled ability to customize the spectrum of light, enabling a wide range of color temperatures and hues. This flexibility is crucial in settings where color accuracy is paramount, such as in retail displays, art galleries, and photography studios, where the faithful representation of color can make a significant difference. Moreover, the capacity of LEDs to mimic natural light patterns supports human circadian rhythms, contributing to well-being and comfort, making them a smart choice for residential and workplace environments alike.
Design and Operational Flexibility
LEDs redefine flexibility in lighting with features like seamless dimming and instant-on capabilities. Unlike traditional lighting, which may suffer in lifespan or responsiveness due to dimming, LEDs maintain their efficiency and longevity even when dimmed, offering users complete control over lighting levels without compromise. This instant adjustability, combined with the immediate illumination that LEDs provide, enhances user experience, allowing for dynamic lighting environments that can adapt to any need or occasion.
The design possibilities with LEDs are virtually limitless, thanks to their compact size and directional lighting capabilities. LEDs enable the creation of lighting solutions that range from minimalist and integrated to bold and statement-making. This adaptability allows designers and homeowners to tailor lighting not just to functional requirements but to aesthetic preferences, elevating LEDs from mere light sources to integral components of interior and architectural design.
Disadvantages and Challenges of LED Lighting
While the benefits of LED lighting are numerous and compelling, like any technology, it is not without its drawbacks and challenges. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing the use of LED lighting solutions.
Technical and Performance Limitations
1. Heat Sensitivity and Potential for Overheating
Contrary to the common perception that LEDs do not produce heat, they do generate a certain amount of heat at the semiconductor junction. While this is significantly less than traditional light sources, improper management of this heat can lead to decreased efficiency and shortened lifespan of the LED. High-quality LED fixtures are designed with heat sinks and other thermal management systems to dissipate heat effectively. Proper installation and ensuring adequate ventilation can further mitigate the risk of overheating, preserving the performance and longevity of LED lighting systems.
2. Compatibility Issues with Existing Fixtures
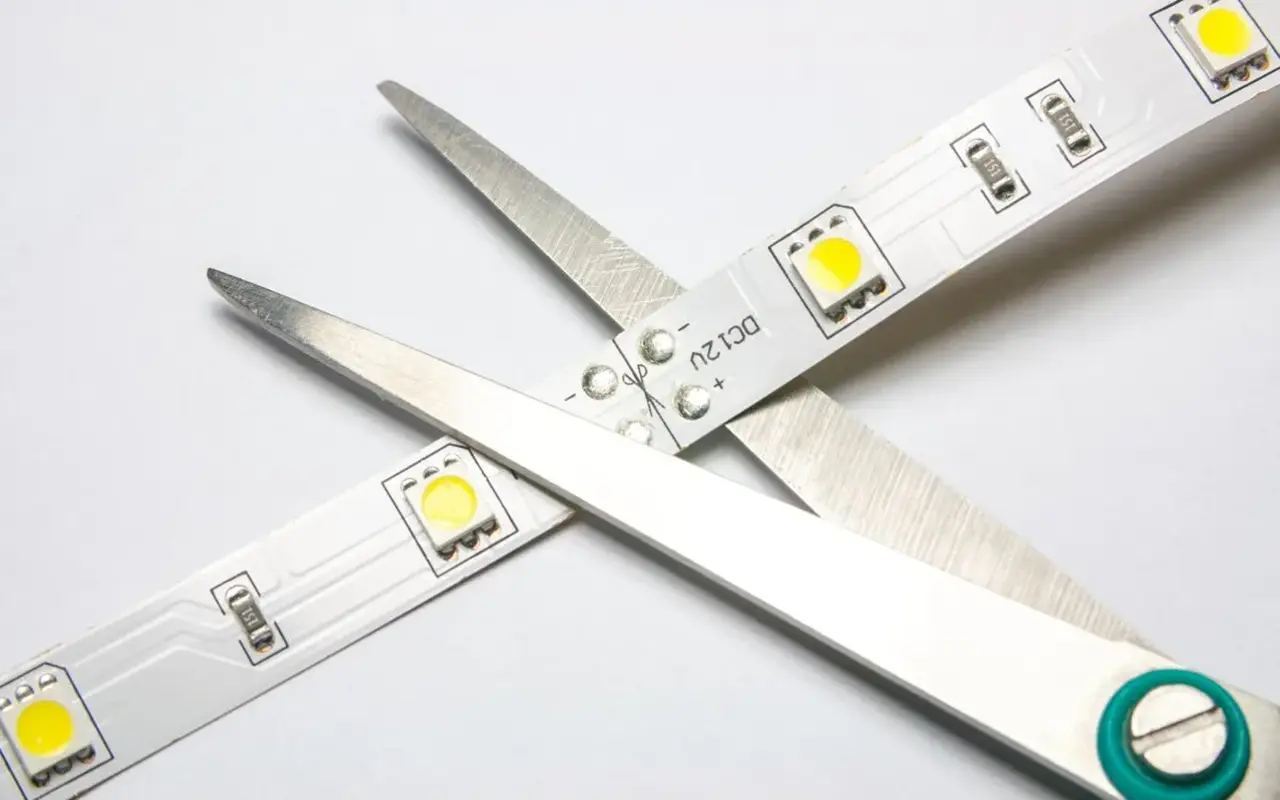
The integration of LED bulbs into fixtures originally designed for incandescent or fluorescent lights can present compatibility challenges. Issues can arise with existing dimming systems, where the electrical characteristics of LEDs may not match those of traditional bulbs, leading to flickering, reduced dimming range, or even failure to function. Additionally, the physical design of some LED bulbs may not fit all fixtures, particularly older or antique ones. Retrofitting with LEDs may require a careful selection of compatible bulbs or modifications to the fixtures, which can sometimes increase the overall cost and complexity of transitioning to LED lighting.
Potential Health and Environmental Risks
1. Blue Light Hazard and Photobiological Safety
A growing body of research has highlighted potential concerns regarding the blue light emitted by some LEDs. Exposure to high levels of blue light, especially during evening hours, can disrupt natural sleep patterns and may have long-term implications for eye health. This has led to increased scrutiny of LED lighting used in environments where exposure occurs in the hours leading up to bedtime. Opting for LEDs with warmer color temperatures and utilizing dimming features in the evening can help mitigate these risks, promoting healthier lighting environments.
2. Radiation Effects and Fire Safety Considerations
While the risk is minimal, LEDs, like all electronic devices, emit a certain level of electromagnetic radiation. Adherence to safety standards and guidelines is essential to minimize any potential risks associated with this radiation. Additionally, although rare, there have been instances of LEDs contributing to fire hazards, particularly when poor-quality products are used or when installed improperly. Choosing high-quality LED products and ensuring professional installation can significantly reduce these risks, ensuring the safe use of LED lighting.
Innovations and Future Trends in LED Lighting
The landscape of LED lighting is one of continuous innovation and evolution, with new advancements promising to further enhance the capabilities and applications of LED technology.
Advances in LED Technologies
The frontier of LED technology is being pushed forward by groundbreaking research and development. Innovations such as Organic LEDs (OLEDs) and quantum dots are redefining the possibilities of LED lighting, offering solutions that are thinner, more flexible, and capable of delivering a broader spectrum of colors with higher accuracy. These advancements are paving the way for new applications of LEDs, from ultra-thin displays to lighting solutions that can be seamlessly integrated into architectural elements.
Smart Lighting and IoT Integration
The convergence of LED lighting with smart technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we interact with light. Smart LED systems, controllable via smartphones, voice commands, or automated settings, are enhancing user convenience and energy efficiency. These intelligent lighting solutions can adapt to users’ needs and preferences, change colors, and integrate with other smart home devices for a cohesive and interactive home environment. The future of LED lighting lies in its ability to become an integrated part of our connected lives, offering not just illumination but also contributing to the overall intelligence of our living and working spaces.
Selecting the Right LED Solutions
Navigating the world of LED lighting requires an understanding of several key factors to ensure the chosen solutions align perfectly with your specific needs and preferences. Whether you’re lighting a cozy living room, a bustling office space, or an outdoor landscape, the right LED lighting can transform the ambiance and functionality of any space.
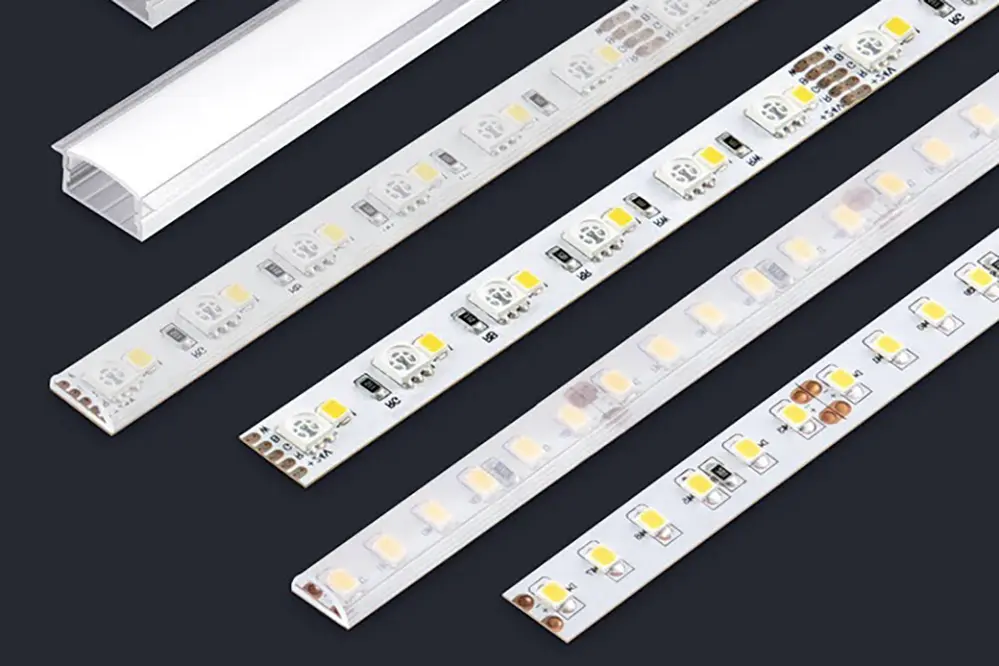
Criteria for Choosing LED Lights and Strips
When embarking on the journey to select the ideal LED lighting, it’s crucial to start with a clear understanding of your intended application and the ambiance you wish to create. Are you aiming for a bright, vibrant workspace or a warm, inviting home environment? The brightness of an LED, measured in lumens, will be a pivotal factor in achieving the desired intensity of light. Lumens offer a direct measure of the amount of light emitted by the LED, guiding you to a choice that ensures your space is neither underlit nor overwhelmingly bright.
Color temperature, measured in Kelvin, plays a significant role in setting the mood of a space. Lower Kelvin values yield a warmer, more inviting light, ideal for living rooms or dining areas, while higher Kelvin values produce a cooler light that enhances concentration and productivity, making them suitable for offices or task-oriented areas.
The Color Rendering Index (CRI) is another critical specification, especially in settings where color accuracy is paramount. A higher CRI value signifies better color fidelity, ensuring that the colors in your space appear true to life under the LED lighting. This feature is particularly important in retail settings, art studios, and anywhere else where color perception can influence mood, aesthetics, or functionality.
Understanding Specifications: CRI, Lumens, and Color Temperature
Delving deeper into the specifications, CRI, lumens, and color temperature become invaluable tools in the selection process. A high CRI value, typically above 80, is desirable for most residential and commercial applications, ensuring that the colors within the space are rendered accurately and vibrantly.
Lumens are your guide to brightness, helping you navigate the balance between cozy, subdued lighting and bright, energizing illumination. The choice of lumens will depend on the size of the space and the activities it hosts, ensuring that the lighting is both effective and efficient.
Color temperature, with its spectrum from warm to cool, allows you to sculpt the ambiance of a space to your liking. Warmer temperatures, around 2700K to 3000K, create a welcoming atmosphere, while cooler temperatures, above 4000K, foster focus and alertness.
Practical Applications of LED Lighting
The practical applications of LED lighting are as diverse as they are innovative, catering to a wide array of needs across residential, commercial, and industrial domains.
Residential, Commercial, and Industrial Uses
In residential settings, LEDs offer the flexibility to create environments that are both functional and atmospheric, from the focused lighting needed in a home office to the warm glow desirable in a living area. Commercial spaces benefit from LEDs through enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs, with tailored lighting solutions supporting various business activities. In industrial environments, the durability and energy efficiency of LEDs contribute to safer, more reliable operations, with lighting solutions designed to withstand demanding conditions.
Outdoor Lighting and Specialized Applications
Outdoor applications of LED lighting extend from aesthetic landscape lighting that enhances architectural features and garden designs to practical street lighting that ensures public safety. The robustness of LEDs makes them ideal for withstanding outdoor conditions, providing reliable lighting that contributes to both beauty and security.
Specialized applications of LEDs are seeing significant growth, with advancements in technology enabling their use in areas like horticulture, where specific light spectra promote plant growth, and healthcare, where lighting can be tailored to support patient recovery and well-being.
Conclusion
The journey through the world of LED lighting reveals a landscape rich with benefits that significantly outweigh the challenges. The initial cost and technical considerations associated with LEDs are minor when viewed against the backdrop of their energy efficiency, environmental benefits, and the vast array of applications they support. As technology continues to advance, the future of LED lighting shines bright, promising even greater innovations and solutions that will continue to transform our illuminated world, making LEDs the unequivocal choice for a sustainable, versatile, and vibrant lighting future.
For those delving into the dynamic world of LED lighting, partnering with a trusted expert like Unitop, a leading manufacturer of LED strip lights and LED neon flex in China, is key. With a wealth of experience and a commitment to quality, Unitop is ready to assist with any inquiries or specific needs you may have. Contact us today and illuminate your space with confidence and expertise.

Tom is now the Sales Manager of Unitop (China) Co., Limited. He has been in the LED Lighting industry ever since 2005. He is an expert in sales & marketing, and factory management. He likes bodybuilding, and he is also a crazy Apple Fan! He is a hard-working guy and loves to learn and try new things.
Email: tom@unitopledstrip.com WhatsApp: +86-18680307140









اترك رداً
تريد المشاركة في هذا النقاششارك إن أردت
Feel free to contribute!